- automatics.AI

- Aug 22, 2025
- 10 min read
Updated: Aug 26, 2025
How intelligent automation protects your business-critical data
A recent SAPinsider study from 2025 shows alarmingly clear evidence: 92% of surveyed companies consider their SAP systems mission-critical, yet only 34% have a mature cybersecurity posture. This discrepancy between critical business processes and the actual level of security highlights the urgent need for action.
At a time when cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and compliance and system availability requirements are increasing, SAP Basis teams are under enormous pressure. The study, conducted between March and May 2025, included companies of various sizes and across industries – from manufacturing to financial services. The results clearly show: traditional, reactive security approaches are no longer sufficient.
Modern automation solutions such as the automatics SmartSecOps Platform are therefore becoming a decisive success factor for a proactive SAP security strategy.
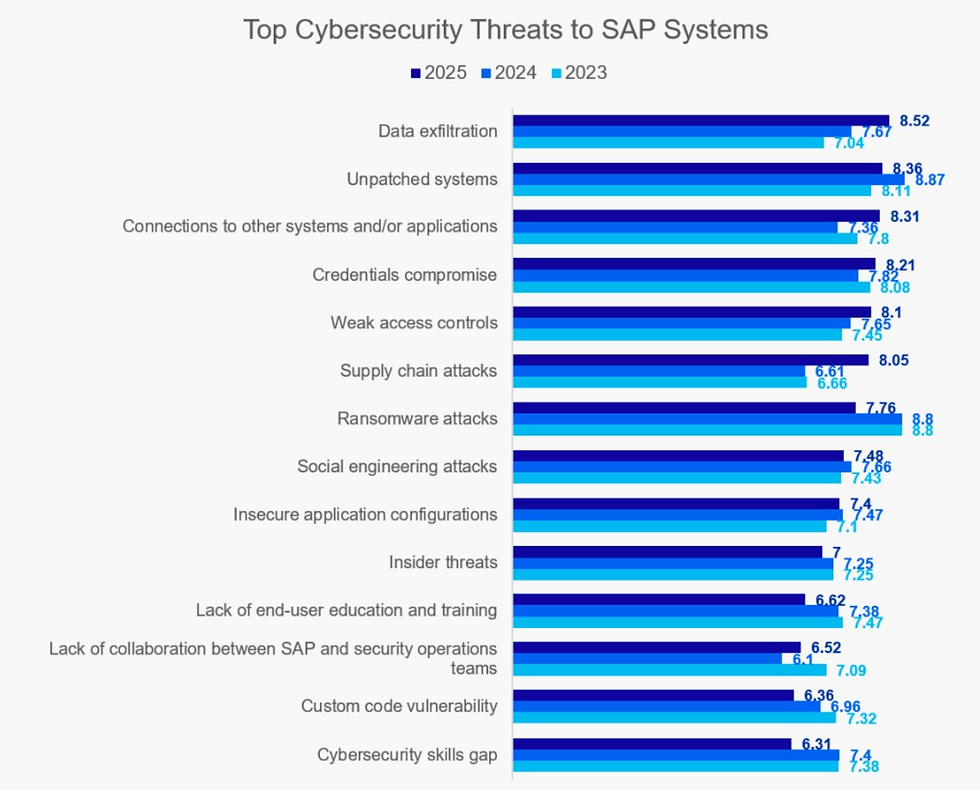
1. Data Exfiltration - The new number one cyber threat
With a threat index of 8.52 out of 10, data exfiltration tops the list of the most serious cybersecurity threats for the first time. This dramatic increase compared to the previous year (7.04 points) reflects concerns that attackers are deliberately targeting valuable corporate data in SAP systems.
The threat landscape has fundamentally changed: Modern attackers are no longer focused solely on system compromise, but on the precise extraction of highly sensitive business data. SAP systems are particularly attractive targets because they typically house the most valuable corporate data: complete customer databases with payment information, detailed financial reports, strategic business plans, supplier data, and operational metrics. This risk increases in hybrid-cloud environments where data is transferred between different systems.
The effects of successful data exfiltration are devastating: In addition to direct financial losses due to ransom demands, massive compliance penalties (GDPR fines can amount to up to 4% of annual turnover) are incurred. Reputational damage leads to customer loss, trade secrets fall into the wrong hands, and can permanently weaken a company's competitive position. Particularly dramatic: The average global damage from data theft reached a record high of USD 4.88 million in 2024 , with an even more dramatic increase to 10.22 million USD in the US in 2025.
Reality Check: Current Threat Situation
CVE-2025-31324 Exploitation : 581 SAP NetWeaver instances were compromised by Chinese APT groups via the critical vulnerability CVE-2025-31324 . The vulnerability has a CVSS score of 10.0 and allows attackers to upload files without authentication.
Ransomware attacks on SAP : Since 2021, there has been a 400% increase in ransomware attacks directly compromising SAP-based data. Leading ransomware groups such as Conti, Quantum, LockBit, Blackcat, HIVE, REvil, and Netwalker have been involved.
Exploit prices are rising : Prices for remote code execution (RCE) attacks on SAP applications increased by 400% from 2020 to 2023. Exploit brokers are offering up to $50,000 for RCE exploits against SAP NetWeaver-based systems, with current prices reaching $250,000.
How the automatics SecurityHub prevents data exfiltration
The SecurityHub implements context-based data classification directly in SAP applications through seamless integration with Microsoft Purview Information Protection. This integration enables, for the first time, enterprise-grade data protection to be implemented directly in SAP transactions—a revolution for companies that previously relied on separate solutions.
All data exports are automatically monitored and protected with policy-driven safeguards. Zero-trust principles are consistently enforced at the document, table, and transaction levels. A particularly valuable feature is that the solution works for both traditional on-premises environments and modern cloud and hybrid deployments. Sensitive data remains protected even after export, and regulatory requirements such as GDPR, DORA, and NIS2 are automatically met.
2. Unpatched Systems - The Permanent Security Risk
Unpatched systems represent the second-highest threat, scoring 8.36 points, and represent a systemic problem in the SAP landscape. Thirty-five percent of respondents stated that the timely application of SAP Security Notes is their greatest challenge. Particularly problematic: 57 percent have difficulty validating whether patches have been implemented correctly.
The complexity of SAP patch management is unique: Security notes can have complex dependencies, require specific implementation sequences, and often impact critical business processes. A single incorrectly implemented patch can bring productive systems to a standstill, which is why many companies choose a reactive approach—with catastrophic security consequences.
The impact of unpatched systems is measurable: Known vulnerabilities are systematically exploited by attackers, automated scanning tools identify vulnerable systems within hours of security notes being published. According to recent studies, 60% of all data breaches are due to unpatched vulnerabilities , and Companies with delayed patch management cycles of more than 30 days have a significantly higher probability of successful cyberattacks . Compliance violations are inevitable, as auditors increasingly consider timely patch management a critical evaluation factor.
Reality Check: Current Patch Landscape
CVE-2025-31324 Timeline : On April 29, 2025, CVE-2025-31324 was added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog . SAP released an emergency fix.
Monthly Security Notes : In March 2025, SAP published 21 new security notes , In July 2025 there were 27 new security notes . SAP has introduced a regular Security Patch Day on the second Tuesday of every month .
Critical vulnerabilities 2025 : In January 2025, two HotNews vulnerabilities with CVSS score 9.9 were published , and in April three more HotNews notes with CVSS scores up to 9.9 were added .
Lifecycle and OperationHub solve the patching dilemma
The Lifecycle Hub automates the entire process from SAP Security Note identification to documentation. The system performs automatic downloads, checks relevance for the specific SAP landscape, and analyzes complex dependencies between notes. This is crucial because security notes are often interdependent and must be implemented in the correct order.
The OperationHub complements this with secure, automated patch deployment during optimal maintenance windows. This not only applies the patches themselves, but also performs all necessary pre- and post-patch work automatically. All activities are fully documented and audited, enabling seamless tracking for compliance purposes. This end-to-end automation significantly reduces the risk of human error.
3. Connections to other systems - The underestimated attack surface
With a score of 8.31, system connections reflect the reality of networked IT landscapes, but are systematically underestimated as a threat vector. Every interface to third-party systems—from reporting tools to IoT sensors—represents a potential attack surface. In cloud and hybrid environments, this complexity grows exponentially.
Modern SAP landscapes are highly interconnected: Business intelligence tools tap data, CRM systems synchronize customer data, e-commerce platforms transmit orders, IoT sensors from production send machine data, and cloud services extend functionality. Each of these connections can be configured as "trusted," but at the same time represent a backdoor for attackers.
The effects of compromised system connections are particularly insidious: Attackers use "living off the land" techniques , moving laterally through trusted connections and often remaining undetected for months. The infamous SolarWinds attack demonstrated how third-party system connections can be used to compromise over 18,000 organizations . By compromising a single trusted software update chain, attackers gained access to thousands of government agencies and companies . In SAP environments, the impact is even more dramatic, as core business processes are affected.
Reality Check: Complex Attack Vectors
Multi-vector attacks : China-linked threat actor Earth Lamia exploits up to eight different vulnerabilities to compromise publicly accessible servers , including CVE-2025-31324 in SAP NetWeaver, but also vulnerabilities in GitLab, WordPress and other systems.
Supply chain risks : Chinese state-backed APTs launched high-frequency exploitation campaigns against critical infrastructure networks via SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer in April 2025 , aiming for lateral movement into industrial control systems (ICS).
Internet-exposed systems : Onapsis Research Labs identified more than 10,000 internet-facing SAP applications that may be affected by the CVE-2025-31324 vulnerability , with estimates that 50%-70% of these applications have the vulnerable component enabled.
TransparencyHub creates visibility and control
The Transparency Hub captures, analyzes, and visualizes all security-relevant SAP system data and interfaces. It provides a holistic overview of the entire SAP landscape—regardless of whether systems are operated on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid environments.
The system makes all connections to external systems transparent and continuously monitors them for anomalies. Complex dependencies are visualized in intuitive dashboards, allowing security teams to quickly identify potential attack paths. Real-time monitoring and comprehensive reporting enable preventative measures to be taken before vulnerabilities are exploited. This proactive approach is crucial in modern, interconnected IT landscapes.
4. Weak Access Controls - The Foundation of SAP Security
Weak access controls score 8.1 points and often develop gradually over years due to organizational failure. Employees change positions, temporary access becomes permanent, and the principle of minimum authorization is abandoned. The complexity of SAP authorization concepts often leads to excessively broad authorizations—following the motto "the main thing is that it works."
SAP authorizations are notoriously complex: Over 12,000 authorization objects, hundreds of transaction codes, and complex role hierarchies create a labyrinth that overwhelms even experienced administrators. Administrators often grant overly extensive authorizations to avoid disruptions. The result: Regular users frequently have access to sensitive transactions such as master data changes, financial reports, or even system configurations.
The consequences of weak access controls are dramatic: they enable insider threats, inadvertent data manipulation leads to business damage, and external attackers can abuse extensive permissions after initial compromise. According to recent studies, up to 60% of all security incidents are enabled by excessive or incorrectly configured user permissions . Compliance violations are inevitable, especially in regulated industries such as financial services or pharmaceuticals.
Reality Check: Authorization Management in Practice
SAP Authorization Complexity : SAP Security Note #3563927 with CVSS score 8.8 addressed a critical vulnerability in transaction SA38 of SAP NetWeaver Application Server ABAP that allowed access to Class Builder functionality that should be restricted to the ABAP Development Workbench.
Authorization Bypass Vulnerabilities : In April 2025, SAP Security Note #3572688 with CVSS score 9.8 was published, which patches an authentication bypass vulnerability in SAP Financial Consolidation.
Missing Authorization Checks : Onapsis Research Labs contributed to the patching of remote-enabled function modules that did not check for appropriate authorizations, allowing authenticated attackers to obtain otherwise restricted information.
SecurityHub: Data protection for SAP exports according to zero-trust principles
The SecurityHub protects sensitive SAP data during export through context-based data classification and policy-driven security measures. The SecurityHub continuously monitors all exports (such as downloads, prints, and send mail) for sensitive SAP data and applies customizable authorization rules as needed. Context-based factors such as user behavior, system status, and data sensitivity are taken into account. Document-, table-, and transaction-based access controls enable significantly finer control than traditional role-based approaches.
5. Insecure Application Configurations - The Overlooked Vulnerabilities
Insecure application configurations ranked fifth with 7.4 points and represent a systemic problem in SAP administration. SAP systems offer thousands of configuration parameters, often managed by different teams without a central security strategy. Standard configurations are often adopted unchanged into production environments—a fatal mistake.
The problem is complex: SAP systems are delivered with developer-friendly default settings that are unsuitable for production environments. Debug modes remain active, logging levels are inappropriate, and network access is configured too permissively. Different teams (Basis, Security, and business units) have different configuration responsibilities without central governance. Changes are often made ad hoc, without security reviews or documentation.
The effects of insecure configurations are often subtle but devastating: Attackers exploit misconfigurations for initial access, debug interfaces enable code execution, excessive logging activities expose sensitive information, and weak encryption settings enable man-in-the-middle attacks. The insidious aspect: Many vulnerabilities are not obvious and are only discovered during targeted security assessments or after successful attacks.
Reality Check: Configuration Vulnerabilities in SAP
Vulnerable Components : SAP Security Note #3569602 with CVSS score 8.8 patched a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in SAP Commerce caused by the swagger-ui open source library.
Spring Framework Security : SAP Security Note #3576540 provides best practice information for customized Java applications in SAP BTP implemented with the Spring Framework to prevent sensitive endpoints, typically used for debugging purposes, from becoming accessible.
Deserialization Vulnerabilities : CVE-2025-42999 is a deserialization vulnerability affecting SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer Development Server. An authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to achieve code execution on affected hosts.
OperationHub ensures secure configurations
The OperationHub continuously monitors all security-relevant configurations through automated SAP Profile Parameter Management. This encompasses the complete control of SAP system operations – from controlled startup and shutdown of SAP instances to secure updates of operating systems and databases to the optimal configuration of all system parameters for maximum security and performance . Predefined security profiles are automatically applied, and deviations are detected and corrected. Cross-platform support – from various operating systems to all common database systems – ensures consistent security standards.
6. Lack of collaboration between SAP and security teams
With a score of 6.52, a lack of collaboration is often the root cause of other security problems and can lead to organizational difficulties. Communication problems can often arise here: SAP teams don't have a complete overview of the threat landscape, while security teams aren't always equipped with the necessary SAP understanding. These silos lead to suboptimal security strategies and can create dangerous gaps in coverage.
The problem is structural: SAP administrators focus on availability and performance, while security teams specialize in threat defense. Differing priorities, terminologies, and responsibilities create communication barriers. SAP-specific security topics are not integrated into overarching security strategies, while general security measures are often not implemented in a SAP-compatible manner.
The effects are measurable: Security vulnerabilities remain undetected longer, incident response is ineffective due to a lack of SAP-specific knowledge, investments in security tools are uncoordinated, and compliance requirements are implemented inconsistently. Studies show that companies with integrated SAP security teams have 45% fewer security-related incidents and 60% shorter incident response times.
Reality check: Integration of SAP Security
Incident Response Challenges : Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 observed suspicious HTTP requests to the /developmentserver/metadatauploader endpoint as early as late January 2025, likely testing this vulnerability before it was publicly disclosed.
Security Research Collaboration : Vendor research labs work closely with SAP to identify and patch vulnerabilities. Two vulnerabilities identified in March 2025 stem directly from vendor research efforts.
SmartSecOps Platform as a bridge between teams
The automatics SmartSecOps Platform acts as an intelligent bridge by providing consistent, comprehensive SAP-specific security data in understandable formats. The Transparency Hub creates a common fact base upon which both teams can build.
Seamless integration with SIEM systems, ITSM workflows, and SOC playbooks enables SAP security events to be automatically integrated into higher-level security processes. This means that SAP systems are no longer viewed as isolated islands, but as an integral part of corporate security.
The platform's modern, intuitive user interface bridges knowledge gaps and enables efficient collaboration between both teams. Monitoring, logging, and reporting are presented in unified dashboards that provide both technical details and strategic overviews.
Conclusion: Intelligent automation as the key to SAP security
The six biggest cybersecurity threats clearly demonstrate that traditional, manual security approaches no longer meet today's requirements. The complexity of modern SAP landscapes, combined with constantly evolving threats, requires a fundamentally new approach.
The automatics SmartSecOps Platform demonstrates a comprehensive, integrated security strategy through the clever combination of five specialized hubs. From automated patch processes to zero-trust implementation and organizational transparency, each hub contributes to a holistic security concept that goes far beyond traditional point solutions.
The future of SAP security undoubtedly lies in intelligent automation. Companies that invest in modern, integrated security solutions today not only create better protection against current threats but also strategically position themselves for future challenges.
For 92% of mission-critical SAP systems, this is not a nice-to-have, but a strategic imperative for sustainable business success.
Sources and further information:



Comments